Assessing Project Health
The necessity of service:
The I Ching states: “Things that are still are easy to handle; things that haven’t revealed their signs are easy to worry about; things that are soft are easy to scatter; things that are small are easy to disperse; prevent problems before they appear; correct them before they become chaotic.” This is meant to advise that things that are still soft, small, and just beginning to develop are always easier to mold and correct. If one is careless and disregards small matters, allowing them to become large and rigid, then correction becomes very difficult, even impossible.
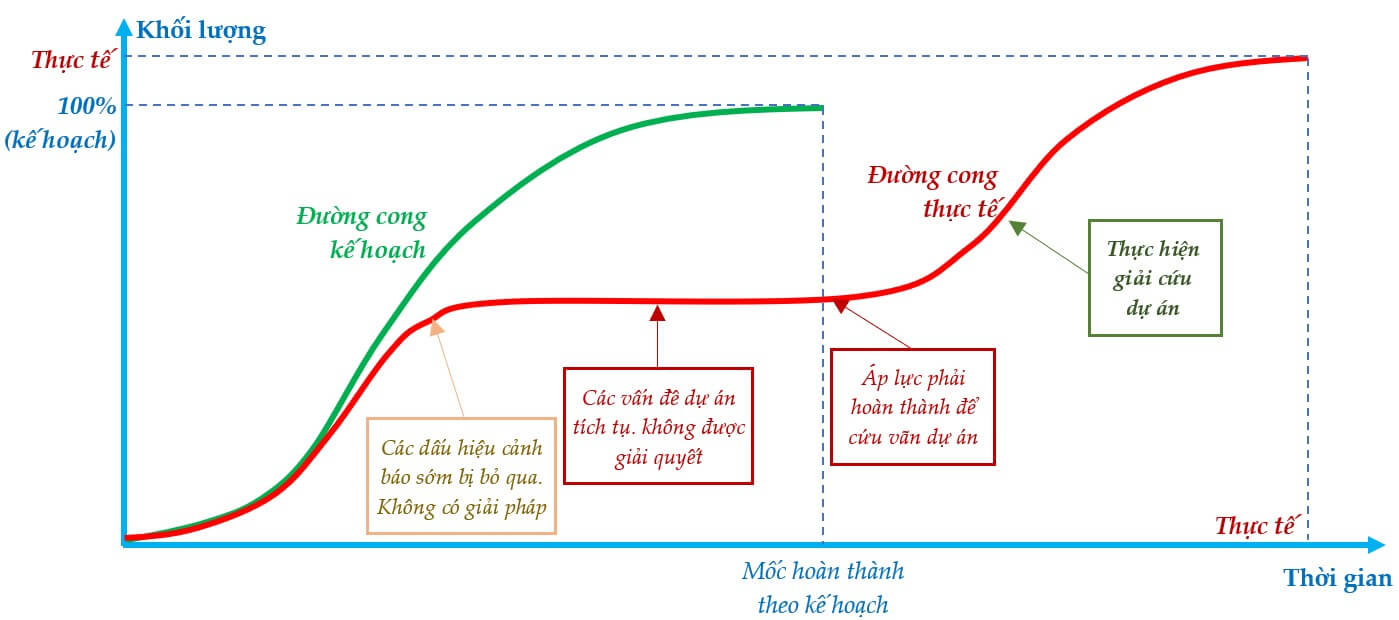
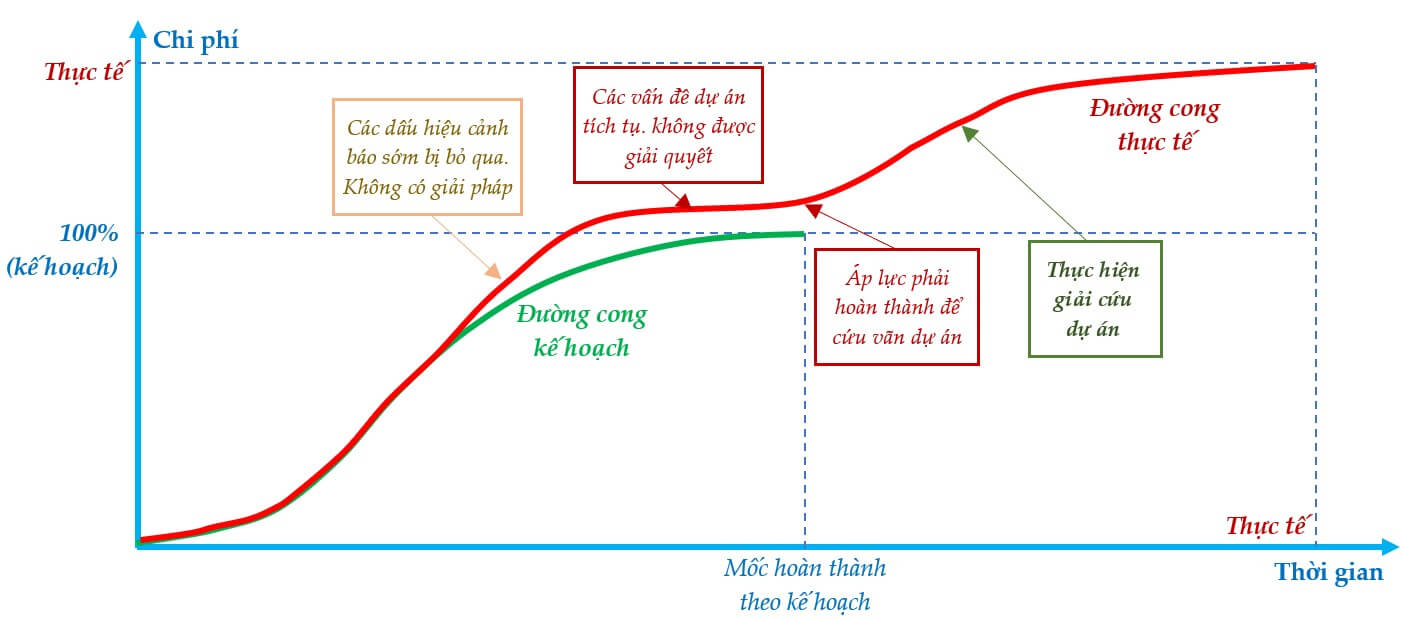
In project management, if early warning signs of project deviations are detected and corrective measures are taken promptly and effectively, the project can easily be brought back on track. If these measures are allowed to persist until the project encounters problems or a crisis and the issues become serious, recovering the project becomes complicated and difficult, resulting in significant delays and increased costs, as illustrated in the following figures.
Benefits for Organizations/ Enterprises:
The PMO and the project health screenings should be conducted periodically and by an independent party. When done appropriately, they offer benefits such as: early detection of problems for timely corrective action; improved project performance; informed decision-making; clear identification of stakeholder responsibilities; proactive risk management; optimization of resource utilization; guaranteed compliance; fostering trust among stakeholders; and promotion of learning and development within the PMO.
Approach:
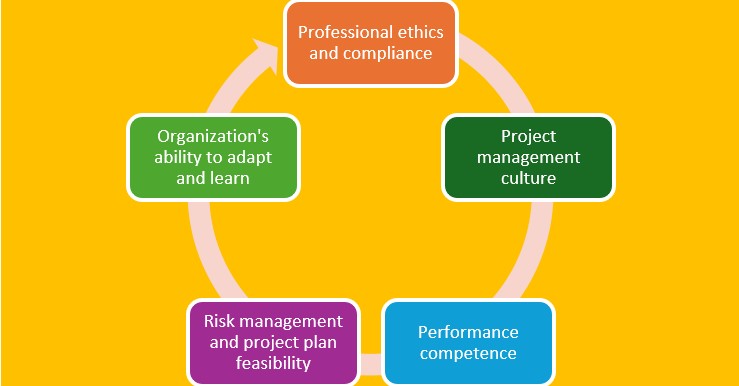
The health of a PMO and its project can be assessed based on five criteria groups: (i) professional ethics and compliance; (ii) project management culture; (iii) performance competence; (iv) risk management and project plan feasibility; and (v) the organization’s ability to adapt and learn.
The PMO and its project health screening requires a systematic approach and transparent communication throughout the assessment process. Several steps should be taken:
- Define the scope, objectives, and evaluation criteria;
- Collect relevant data and information;
- Conduct analysis to identify strengths and weaknesses, as well as potential opportunities or threats;
- Prepare a health screening report outlining the current status, trends, problems, recommendations, and proposed solutions;
- Communicate and discuss with the project management organization to explain, clarify, and ensure a unified understanding;
- Monitor the implementation of recommendations and proposed solutions.
Methods used in the PMO and its project health screening typically include: document review, interviews, surveys, observations, earned value management (EVM) techniques, and risk and impact matrices.
